arthrosis- a very common disease. It begins to form around the ages of 35 to 50, and in people over 70, this disease manifests itself and is diagnosed to varying degrees75-90%Probability. Orthopedists used to attribute osteoarthritis to age, but now the pathology has become "younger". Ignoring the disease is problematic because over time it can lead to partial or complete immobility and disability.
Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease of the joints and cartilage, which is accompanied by the gradual but steady destruction of cartilage and the growth of bone tissue instead of cartilage.
It is obvious that the joint is the most important part of the musculoskeletal system as it is the link between the bones. The most common are coxarthrosis (pelvis), gonarthrosis (knee) and osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint. Small joints are also affected, such as the hands, wrists and the spine.
What is osteoarthritis?
If we simply explain the nature of this disease, then it is characterized byDestruction and breakdown of the joint structure.The bones that hold the joint are covered on one side with cartilage, which performs a protective function. Thanks to these structures, the bones do not wear out.
There is such a thing asCongruence.These are conditions that ensure painless and effective movement of the bones in the joint. Thus, chondron or cartilage plays one of the main roles in the function of the structures in the joint capsule. It contains synovial fluid, which is regularly secreted by the mucous membrane. This is a very important substance that prevents the occurrence of destructive mutual friction of the articular surfaces. The fluid also ensures the metabolism of the articular cartilage, since its structure lacks such an opportunity. This means that the chondron is supplied with the necessary nutrients and toxins are actively eliminated.
When pathological processes come into play, the cartilage begins to decay. Some doctors believe sodestructiondoes not begin in the chondron, but directly in the bone tissue. Over time, its density decreases catastrophically and the cartilage is destroyed. Osteophytes appear on the bone - pathological growths that are popularly classified as so-called slags or salt deposits. In reality, this is completely wrong.
After the destructive process gradually destroys the joint mechanism, nature's compensation strategy kicks in and fills the resulting gap with useless fibrous tissue. It serves no functions in the body and only creates unnecessary stress. In advanced cases, the connective tissue fills all available space and blocks movement completely. This condition is called ankylosis, i. e. H. a fusion of all joints. The joint as well as tendons, muscles, etc. are deformed externally and internally.
Causes of osteoarthritis
Every orthopedist will name the main reason for the development of osteoarthritis: wear and tear on the joints due to insufficient load, metabolic failure or simply time. Several risk factors can also be combined.
Here are the most important ones:
- Unfavorable genetics.
- Older age.
- Vitamin deficiency (calcium deficiency).
- Physical inactivity.
- History of trauma.
- Diseases that destroy connective tissue.
- Obesity.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Insufficient strain during sports.
- Orthopedic pathologies.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
- Occupational deformation on a physical level.
- Pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
- Congenital anomalies of the joint structure.
Several of these factors can be present, which greatly increases the risk of osteoarthritis. If a person suffers from scoliosis, joint dysplasia or rheumatism, arthrosis in this case is considered secondary, since another disease led to its appearance.
It is worth noting that uncomfortable or poor-quality shoes can lead to this dangerous disease.
As for occupational deformity, some people perform a series of stereotypical, repetitive movements over a long period of time due to their work. For example, osteoarthritis of the wrist is most likely to affect mechanics, and osteoarthritis of the knee joint is most likely to affect loaders who carry heavy loads. Ballerinas suffer from ankles and drivers suffer from shoulders.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
pain– the most important symptom of osteoarthritis. When bones rub without synovial fluid and cartilage, this is bound to happen. The pain may subside slightly when at rest, but may increase with exertion. It also occurs at night, promoted by reduced circulatory activity and congestion.
Pain in osteoarthritis can be divided into several types:
- Pain in the morning.It is also called starting symptom and such discomfort occurs after waking up. However, it is short-lived and later disappears when the person dissipates.
- Mechanical complaints.Typically, this sharp pain occurs due to a blockage or impairment of the joint structure. It's impossible to move with such pain.
- Meteosensitivity. The nature of the pain is clear from the name - it is painful, unpleasant and intrusive; Many people call this condition: "It hurts because of the weather. "
The initial stage of arthrosis passes into a more severe one, and this process is accompanied by constant pain. The skin over the affected joint becomes red, swollen, and hot. Osteoarthritis is characterized by an alternation of exacerbations and remissions, and as the process progresses, the second indicated condition decreases over time and the first increases.
Osteoarthritis often occurs during pregnancy, so a woman is often treated by a traumatologist together with a gynecologist
Skin pigmentation and changes in muscle tone may occur at the site of joint deformation. In addition, depending on the location of the pathology, there are not only difficulties in movement, but also headaches if, for example, osteoarthritis has occupied the cervical vertebra.
Classification of osteoarthritis
First of all, it depends on the localization of the pathology. Most often these are the spine and the lower or upper limbs. The knee and hip joints are subject to enormous strain and are therefore statistically the most affected. By the way, the first of the osteoarthritis foci mentioned is the most characteristic of the female body.
Spondyloarthrosis is often diagnosed in the spine area. It is characteristic of the lumbar region. A person in such situations has difficulty carrying loads and cannot stand for a long time. The diagnosis of non-concealed osteoarthritis occurs when the cervical spine is affected.
Osteoarthritis in the elbow and shoulder joints is relevant for the lower extremities. This is not surprising as the locations mentioned are subject to increased trauma and stress.
Depending on the nature of its occurrence, osteoarthritis is divided into:
- Primary.
- Secondary.
In the first case it is an imbalance between the synthesis and degeneration of joint tissue, in the second case it is the appearance of arthrosis against the background of previous diseases as a complication.
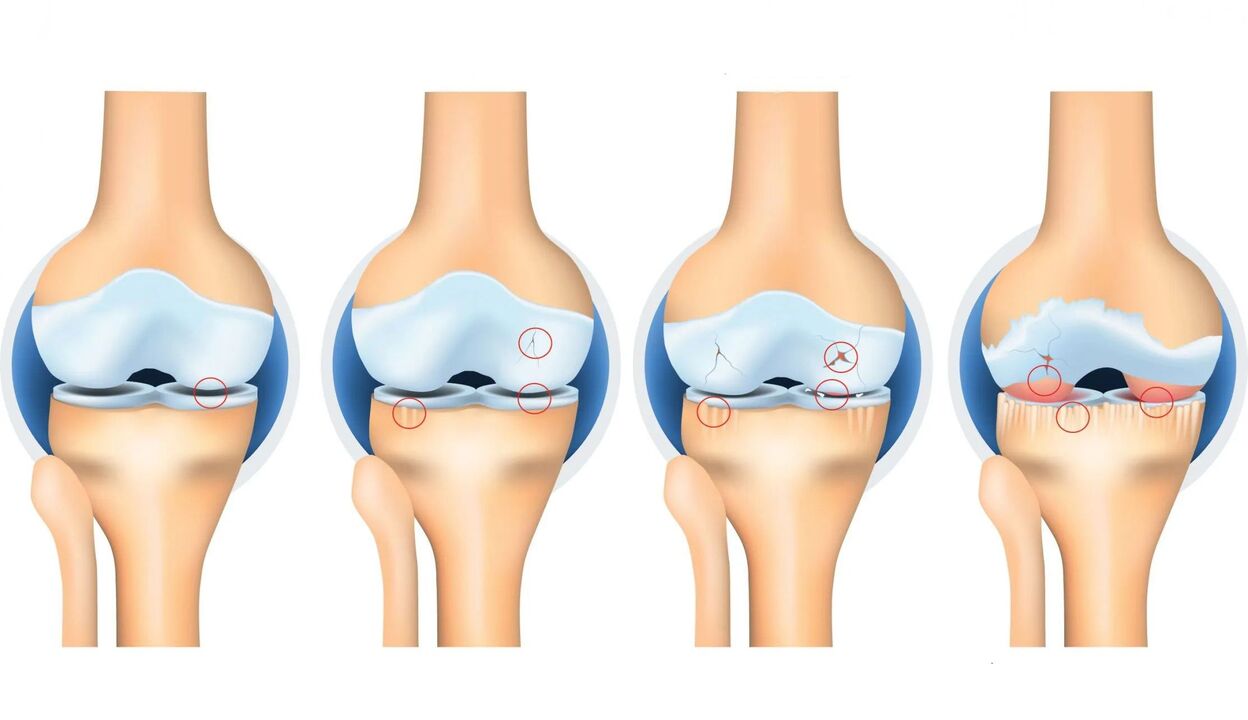
There are also different degrees of osteoarthritis. There are only five of them, the first of which is zero and has no external signs of the disease.
- 1st degree osteoarthritis.It is characterized by a barely noticeable narrowing of the joint space.
- Osteoarthritis 2 degrees.At this stage, the situation becomes slightly worse: the gap does not narrow any further, but uneven surfaces of the joint appear.
- Osteoarthritis 3 degrees.Here all of the above signs are intensified.
Fourth degree osteoarthritis involves necrosis of bone tissue and deformation of the joint. When treating osteoarthritis, it is important to take the degree of the disease into account in order to enable better treatment planning.
Stages of osteoarthritis
The disease progresses in three stages.
- First stage.The condition is characterized by a slight limitation of movement and the appearance of osteophytes that are almost invisible on examination.
- Second floor.At this stage, the mobility of the joint is even more limited, a crunch occurs when moving and growth on the bones increases. Mild atrophy of muscle tissue may occur.
- Third section.The joint is deformed and this can also be seen externally. The patient's movement is very difficult, the joint space practically disappears, and the osteophytes are significant. Cysts are sometimes observed.
How is osteoarthritis diagnosed and treated?
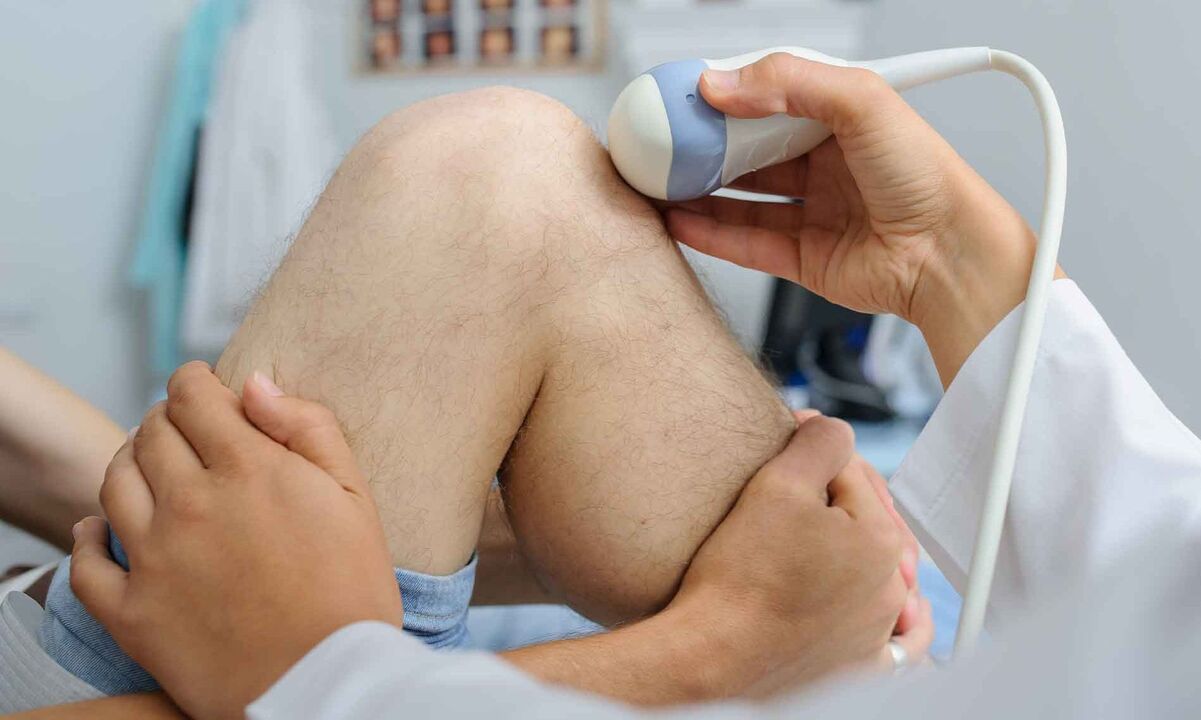
Treatment of this disease, which is widespread on the planet, requires a number of diagnostic procedures. But first the patient is questioned and examined. In the advanced stage, deformations of the joint, changes in its contour are visually visible and the patient complains of difficulty in movement.
The following diagnostic tests are prescribed:
- Roentgen.
- MRI.
- Ultrasonic.
An X-ray examination can show the condition of the joint spaces and the growth of bone tissue, but fibrous structures are not visible with this diagnostic method. Magnetic resonance imaging is used for this purpose.
However, ultrasound examination is very informative in the first and second stages of arthrosis, as the most minimal and insignificant changes in the joint structure can be seen.
The treatment of osteoarthritis is divided intoconservative and surgical. The first type is about relieving pressure on the joint, which is its main goal. To do this, it is necessary to carry out a series of therapeutic exercises and lifestyle adjustments (excluding heavy lifting, etc. ). If excess weight has led to osteoarthritis, therapeutic measures are particularly aimed at thisWeight loss of the patient.In the early stages of osteoarthritis, increasing physical activity, even if it is moderate, helps a lot. Cycling, swimming, therapeutic walking – doctors use all of these in the conservative treatment of the disease.
As for medications, they are relevantChondroprotectors or hyaluronic acid– They are injected directly into the joint. This stops the progression of the disease and prevents further breakdown of the joint components. They use hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthetics and drugs to improve the microcirculation of biological fluids.
Muscle tone is increased through physiotherapy, e. g. b.UHF or phonophoresis.Massages are also used, especially as directed by a doctor.
The gold standard of treatment is arthroscopy. A special device, an arthroscope, is inserted into the joint cavity. Thanks to technical possibilities, its internal structure is made visible, so the surgeon removes dead tissue, polishes the surfaces, washes the cavities, in short, performs mechanical reconstruction.
If synovitis occurs, the fluid must be pumped out, which is why a joint puncture is used. As part of the procedure, medication is also administered to restore the functionality of the motor unit.
The most radical type of intervention isEndoprosthetics. It is used when there is no other way to influence the joint. This usually happens in advanced cases. The endoprosthesis replacement is suitable for both the hip joint and the knee.
Prevention of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a chronic and irreversible disease whose development can still be stopped or significantly slowed down. Preventive measures include measured and sensible physical activity, avoiding physical inactivity or overexertion. This is particularly important for representatives of the professional groups mentioned above. You should also treat diseases of the orthopedic system in a timely manner, avoid critical weight gain and wearing uncomfortable shoes.
Diet for osteoarthritis
Diet plays a crucial role in osteoarthritis. Doctors recommend eating poultry as a source of protein, dairy products (especially butter), vegetables, grains, nuts and fatty fish.
On the contrary, you should not eat a lot of baked goods made from wheat flour, muffins, confectionery, fast food, salty, pickled, hot and sour dishes. You also need to avoid alcohol and soda. Interestingly, even ice can be harmful for osteoarthritis!
For patients with obesity, fasting is recommended for this pathology under the supervision of a nutritionist.
How do I know if I have osteoarthritis?
In this disease, short-term joint blockages, weather-related pain occur in the morning, and in advanced cases, discomfort is also observed at night when the person does not move. In the first stages, painful sensations are registered when moving, but the pain disappears when at rest.
Is it possible to beat osteoarthritis?
It is impossible to completely cure the disease, but it is possible to stop the degenerative process. The main thing is to see a doctor as early as possible.
What should you not do if you have osteoarthritis of the joints?
You should not put too much strain on your joints by lifting weights and, on the contrary, limit your movements excessively. Consuming fast food, lots of chocolate and ice cream, carbonated drinks, alcohol and marinades is not recommended.